Recycling Equipment
In the last several decades, the recycling industry has seen a steady rise in demand for recycled materials as well as an increase in the number of end-user items and materials facilities are capable of recycling. Businesses, retail locations and manufacturers are realizing the financial and environmental benefits of recuperating lost material, energy and investment by participating in recycling programs and purchasing reconstituted raw materials. Recycling facilities are key in this process, providing a variety of sorting, shredding, baling and refining services. Because recycling processes require many specialized types of equipment, recycling facilities tend to specialize in sorting and baling materials to be shipped out for further processes, or facilities specialize in reclaiming one type of material, such as PET, aluminum cans or cardboard.
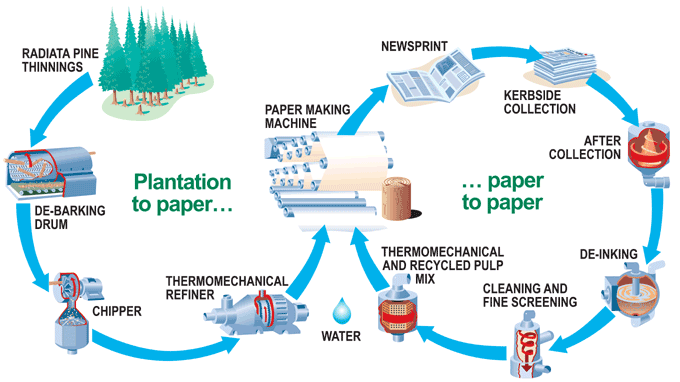
Different types of industrial equipment are used for metal recovery, plastic recovery, pulp recovery and other reclamation processes. Initial sorting stages for material recovery use conveyors, vibratory feeders, magnet assemblies and downstream trommel screens or mixers which separate parts by size and material. While machine vision systems may be employed for robotic sorting, the most cost-effective methods of sorting materials involve both conveyorized screening and manual sorting. Once sorted, materials are reduced in size by shredders, grinders or pulverizers, mixed with water and/or refining chemicals, melted, extracted and re-extruded, rolled or forged into raw plastic pellets, metal ingots or paper rolls.
Aside from traditional paper, plastic, glass and metal recycling, there are facilities capable of recycling consumer items such as ink cartridges, batteries, light bulbs, carpet and computers as well. Recycling may also be employed on a smaller scale within manufacturing facilities for the reclamation of materials and energy lost during processing. Dust collectors or downdraft tables, for example, may collect fine metal shavings lost during metal parts machining; heat exchangers capture the heat energy lost from one process and re-uses it in other processes. Many non-recyclable materials may still be recycled for energy through incineration and waste heat recovery systems.
|
 |






